Introduction
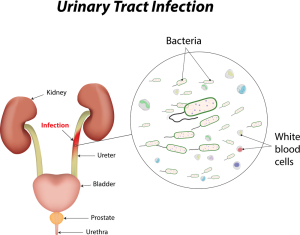
The urinary tract starts with the kidneys. These are connected via the ureters to the bladder. From there the urethra allows the urine to exit. Each of these structures can get infected and this is described in more detail under the links below. The function of the kidneys is to detoxify the body. This is achieved by having a network of capillaries distributed through the kidney tissue.
It is there where the filtration system is to purify the blood. There is a sophisticated network of microscopically small renal tubules where the initial urine is collected and then concentrated. The ureters are transporting tubes that transport the urine from the kidneys into the storage chamber of the bladder. When the bladder is full you feel an impulse to go to the bathroom and when you have emptied it, the cycle starts again.
References
These are a few references that describe urinary tract infections in more detail.
1.The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 227.
2.The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 261.
3.The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 164.
4.James Chin et al., Editors: Control of Communicable Diseases Manual, 17th edition, 2000, American Public Health Association.
5. David Heymann, MD, Editor: Control of Communicable Diseases Manual, 18th Edition, 2004, American Public Health Association.