Treatment of gout involves several steps. The table below summarizes this and the text explains it in more detail.
Therapeutic steps in treating gout
|
Treating the pain
The most important step is to treat the acute gout pain with anti-inflammatory medications. This minimizes the soft tissue damage in the body and helps the patient overcome the severe pain. Colchicine is the drug of choice to achieve this, which usually controls the joint pains within 12 to 48 hours. Side-effects of colchicine therapy are diarrhea, which can lead to electrolyte disturbances, and bone marrow suppression. In patients with compromised kidney function the physician must carefully monitor for toxicity as in severe cases of kidney malfunction respiratory depression and cardiotoxic effects could lead to death.
On the other hand colchicine in the appropriate patient can be very effective and impressively takes the pain away through the specific suppression of the inflammatory response to the uric acid crystals. Leukocytes take up colchicine. This stops the inflammatory infiltration of leukocytes, which inhibits kinin release and pain. The gout patient can take colchicine also for prevention of an attack or again when another gout attack flares up. However, colchicine has limits. It does not lower uric acid levels and does not prevent progression to chronic gout.
Lowering the uric acid level
Allopurinol (brand name: Zyloprim, Lopurin) inhibits the synthesis of uric acid and also inhibits the formation of purin in the body. All of this leads to lower serum uric acid levels and your physician can titrate the dosage by repeat blood tests. The level needs to be around 4.5 mg/dL (or 0.26 mmol/L) or lower.
Another approach to lower uric acid levels is to increase uric acid elimination via the urine. The name for this is “uricosuric therapy”. Two medicines serve for this purpose: probenecid (brand names: Benemid and Benuryl) and sulfinpyrazone (brand name: Anturan). Salicylates such as ASA or non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) counteract this uricosuric effect and should be avoided when this medication is given. Your doctor knows best what medication to use in your case and can also explain the allopurinol side effects and side effects of the other drugs.
Control inflammation
In the first few days or weeks the joint inflammation and inflammation of the affected connective tissue is causing a great deal of pain and discomfort. It is here where some anti-inflammatories such as NSAIDs may have a place.
However, as NSAIDs are eliminated through the kidneys and can on the longterm cause a nephropathy (kidney damage) themselves, this needs to be discussed with the treating physician. Kidney function can be assessed by measuring creatinine and BUN levels as well as electrolytes. If there are doubts based on these tests, a 24-hour urine collection can be done to determine the creatinine clearance, which would give a snapshot in time of how well the kidneys are functioning. Every couple of years the creatinine clearance test can be done again to follow the kidney function.
Drugs for gout
Indomethacin (brand name: Indocid) is particularly effective in the acute gouty arthritis, but naproxen (brand names: Naprosyn or Rhodiaprox) is also useful. The COX-2 inhibitory drug (brand name: Celebrex) is also useful. Keep an eye on side-effects of the COX-2 inhibitory medications as one of these drugs (VIOXX) was pulled from the market in October of 2004. The VIOXX link explains this story in detail.
Increased fluid intake
As uric acid is not very soluble, it is advisable to take in fluids of more than 3 L per day, particularly patients who also pass kidney stones (uric acid stones or calcium oxalate stones). Alkalization of the urine also helps and the physician may want to advise the patient to take 500 mg of acetazolamide at bedtime to make the nighttime urine alkaline, which increases solubility for uric acid in the urine and prevents kidney stones.
Other measures
To help with large tophi such as in the elbow region, a surgeon may be able to remove these surgically. But the physician will first attempt to lower uric acid in the blood with medication. Sometimes this helps to dissolve tophi. Also patients with large kidney stones in the center of the kidney (called the “renal pelvis”) can be treated with extra-corporal shock wave lithotripsy, where special ultrasound shock waves cause a resonance and the large kidney stone is broken into sand-like particles that are easily passed with the urine.
Controlling pain
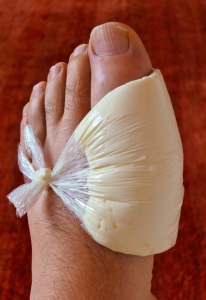
Home remedies for controlling pain are ice packs and “quark packs” as shown in the image of this page. They are simply symptomatic until the effect of colchicine sets in. Physiotherapy treatments are used to remobilize the joints of the foot. Acupuncture may be useful for pain control as well. Anti-inflammatories are used during the acute phase.
References
1. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 55.
2. ABC of rheumatology, second edition, edited by Michael L. Snaith , M.D., BMJ Books, 1999.
3. Goldman: Cecil Textbook of Medicine, 21st ed.(©2000)W.B.Saunders
4. Ferri: Ferri’s Clinical Advisor: Instant Diagnosis and Treatment, 2004 ed., Copyright © 2004 Mosby, Inc.
5. Rakel: Conn’s Current Therapy 2004, 56th ed., Copyright © 2004 Elsevier
6. Suzanne Somers: “Breakthrough” Eight Steps to Wellness– Life-altering Secrets from Today’s Cutting-edge Doctors”, Crown Publishers, 2008