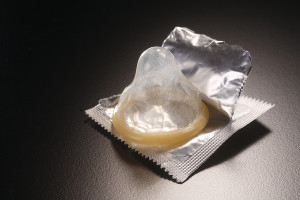
Introduction
The advantage of barrier methods is that the sperm and any bugs (STD’s and AIDS) are largely kept outside the uterine cavity and in the case of male condoms and female condoms are kept out of the vagina as well. This allows for more STD prevention than any other techniques. The best prevention is, of course, some critiques will say, to keep sex just between the same man and woman all the time.
I agree with this viewpoint, but have been witnessing a lot of exceptions to this rule in my clinical experience. Male and female condoms can be applied by the user him- or herself, should be applied before sexual intercourse and has to be handled carefully after sex to dispose of the sperm.
Cervical caps and birth control diaphragms have to be fitted to the internal genital size of the woman by the gynecologist or knowledgeable family physician. Diaphragms should be left in place for 6 hours after intercourse and be used together with a spermicidal cream. Cervical caps can be used for 36 hours not requiring spermicidal cream every time after intercourse as with diaphragm use.
Failure rates can be as high as 10% to 15%. The question is then what to do. The choice is often abortions for these unwanted pregnancies. This is the reason behind the criticism of many churches and ethicists against these methods.
References:
1. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 235.
2. B. Sears: “Zone perfect meals in minutes”. Regan Books, Harper Collins, 1997.
3. Ryan: Kistner’s Gynecology & Women’s Health, 7th ed.,1999 Mosby, Inc.
4. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 245.
5. AB Diekman et al. Am J Reprod Immunol 2000 Mar; 43(3): 134-143.
6. V Damianova et al. Akush Ginekol (Sofia) 1999; 38(2): 31-33.
7. Townsend: Sabiston Textbook of Surgery,16th ed.,2001, W. B. Saunders Company
8. Cotran: Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed., 1999 W. B. Saunders Company
9. Rakel: Conn’s Current Therapy 2001, 53rd ed., W. B. Saunders Co.
10. Ruddy: Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology, 6th ed.,2001 W. B. Saunders Company
11. EC Janowsky et al. N Engl J Med Mar-2000; 342(11): 781-790.
12. Wilson: Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, 9th ed.,1998 W. B. Saunders Company
13. KS Pena et al. Am Fam Physician 2001; 63(9): 1763-1770.
14. LM Apantaku Am Fam Physician Aug 2000; 62(3): 596-602.
15. Noble: Textbook of Primary Care Medicine, 3rd ed., 2001 Mosby, Inc.
16. Goroll: Primary Care Medicine, 4th ed.,2000 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
17. St. Paul’s Hosp. Contin. Educ. Conf. Nov. 2001,Vancouver/BC
18. Gabbe: Obstetrics – Normal and Problem Pregnancies, 3rd ed., 1996 Churchill Livingstone, Inc.
19. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 251.
20. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 250.
21. Ignaz P Semmelweiss: “Die Aetiologie, der Begriff und die Prophylaxis des Kindbettfiebers” (“Etiology, the Understanding and Prophylaxis of Childbed Fever”). Vienna (Austria), 1861.
22. Rosen: Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice, 4th ed., 1998 Mosby-Year Book, Inc.
23. Mandell: Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 5th ed., 2000 Churchill Livingstone, Inc.
24. Horner NK et al. J Am Diet Assoc Nov-2000; 100(11): 1368-1380.
25. Ferri: Ferri’s Clinical Advisor: Instant Diagnosis and Treatment, 2004 ed., Copyright © 2004 Mosby, Inc.
26. Rakel: Conn’s Current Therapy 2004, 56th ed., Copyright © 2004 Elsevier