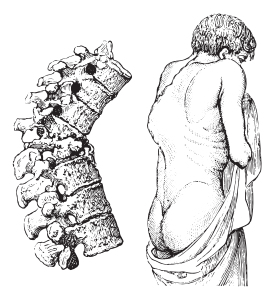
Tuberculosis of bones and joints is particularly common in children where the growth plates are still open for bone growth. TB bacteria find it easy to infect the ends of the blood vessel rich long bones.
The end plates of the vertebral bones are also often involved, a condition called “Pott’s disease”.
The danger here is that the vertebral bodies will collapse when the bone adjacent to the discs is replaced by caseous material, which has no strength.
This can result in paraplegia. However, there are symptoms of bone pain, which warn the patient, the parents and the physician that there is something sinister going on.
At this stage a CT or MRI scan should be done, which will show the suspicious tuberculous lesion.
An orthopedic surgeon should be consulted who can make the diagnosis with a needle biopsy or a laparoscopic biopsy. If there is no paraplegia, then multi-drug antituberculous therapy is given while a stabilizing well fitting spinal brace supports the spine during the healing process. Joints can also be affected through spread into the articular capsule. Weight bearing joints are often involved.
References:
1. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 161.
2. TC Dixon et al. N Engl J Med 1999 Sep 9;341(11):815-826.
3. F Charatan BMJ 2000 Oct 21;321(7267):980.
4. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 43.
5. JR Zunt and CM Marra Neurol Clinics Vol.17, No.4,1999: 675-689.
6. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 162.
7. LE Chapman : Antivir Ther 1999; 4(4): 211-19.
8. HW Cho: Vaccine 1999 Jun 4; 17(20-21): 2569-2575.
9. DO Freedman et al. Med Clinics N. Amer. Vol.83, No 4 (July 1999): 865-883.
10. SP Fisher-Hoch et al. J Virol 2000 Aug; 74(15): 6777-6783.
11. Mandell: Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 5th ed., © 2000 Churchill Livingstone, Inc.
12. Goldman: Cecil Textbook of Medicine, 21st ed., Copyright © 2000 W. B. Saunders Company
13. PE Sax: Infect DisClinics of N America Vol.15, No 2 (June 2001): 433-455.
14. Ferri: Ferri’s Clinical Advisor: Instant Diagnosis and Treatment, 2004 ed., Copyright © 2004 Mosby, Inc.
15. Rakel: Conn’s Current Therapy 2004, 56th ed., Copyright © 2004 Elsevier