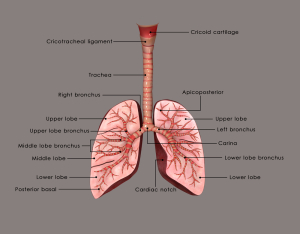
Diagnosis of pneumonia involves blood tests that likely will show an elevation of white blood cells.
In severe cases with a pneumococcal pneumonia blood cultures might be positive for Pneumococcus, a bacterium often associated with pneumonia. Sputum can be sent for Gram staining and preliminary identification of the bacteria in this way can help the physician to decide which antibiotic to use.
A chest X-ray is useful to show an infiltrate indicative of pneumonia. Pneumonias with some bacteria are more commonly prone to develop an abscess, which would show up on X-rays as a lung cavity.
In tuberculosis of the lungs a cavity is a sign that tuberculosis has likely been present for several months.
A good sample of early morning sputum coughed up into a sterile container and then quickly brought to the laboratory can lead to a positive identification of the bacterium that causes the pneumonia in a good number of patients. If the patient does not adequately respond to the therapy, an urgent bronchoscopy should be performed by a respirologist to obtain brushings of cells and material for culture.
References:
1. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 161.
2. TC Dixon et al. N Engl J Med 1999 Sep 9;341(11):815-826.
3. F Charatan BMJ 2000 Oct 21;321(7267):980.
4. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 43.
5. JR Zunt and CM Marra Neurol Clinics Vol.17, No.4,1999: 675-689.
6. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 162.
7. LE Chapman : Antivir Ther 1999; 4(4): 211-19.
8. HW Cho: Vaccine 1999 Jun 4; 17(20-21): 2569-2575.
9. DO Freedman et al. Med Clinics N. Amer. Vol.83, No 4 (July 1999): 865-883.
10. SP Fisher-Hoch et al. J Virol 2000 Aug; 74(15): 6777-6783.
11. Mandell: Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 5th ed., © 2000 Churchill Livingstone, Inc.
12. Goldman: Cecil Textbook of Medicine, 21st ed., Copyright © 2000 W. B. Saunders Company
13. PE Sax: Infect DisClinics of N America Vol.15, No 2 (June 2001): 433-455.
14. Ferri: Ferri’s Clinical Advisor: Instant Diagnosis and Treatment, 2004 ed., Copyright © 2004 Mosby, Inc.
15. Rakel: Conn’s Current Therapy 2004, 56th ed., Copyright © 2004 Elsevier