Introduction
The physician has to take trauma to the eye very seriously.
Here are some statistics of trauma to the eyes (ocular trauma). Depending on the injury it could be very superficial like a laceration to the upper eye lid, which only needs a few sutures in the hospital Emergency Room.
Use of operating microscope for eyelid lacerations
An eye lid laceration that involves the margin of the eye-lid needs a complicated plastic surgical repair utilizing an operating microscope that should be done by an eye surgeon. An eye injury can involve a metal foreign body, which perforated the cornea and entered deep into the eye (“intraocular foreign body”). This is an acute ophthalmic emergency where an eye surgeon has to explore the eye. He/she checks carefully that the anatomy of the lens, the vitreous and the retina were did not experience disruption.
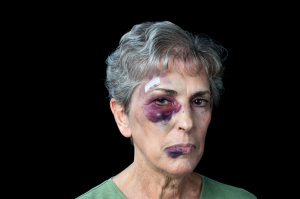
There can also be a blunt eye injury (e.g. airbag injury) or a burn injury, which all need to be carefully evaluated.
Prevention of eye injuries is of the utmost importance.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on what the underlying mechanism of eye injury was. With a chemical injury there would be a burning pain, redness and swelling. With a small abrasion of the cornea from a contact lens injury there would be a foreign body feeling, eye redness and pain.
Diagnostic tests
Ultrasound bio microscopy is a newer tool with which the eye specialist can examine traumatic damage to structures of the eye. Here is an image of the normal eye anatomy using this technology.
Otherwise the eye specialist does the standard diagnostic tests for eye diseases. Direct physical examination amplified by direct ophthalmoscopy and slit lamp examination helps the physician to evaluate most eye injuries. Intraocular pressure test. Ophthalmic ultrasound is useful for the detection of any unusual intraocular mass. To check for the integrity of the retinal blood vessels, a dye can be injected intravenously and subsequently pictures of the fluorescein-stained blood vessels can be taken.
CT and MRI scan for deeper eye injuries
For deeper injuries CT scans and MRI scans may be useful. With this technology we can look through the head of an injured person from the back to the front. We see the brain cavity on top and the left and right eye cavities underneath. The sinus cavities are underneath the eye cavities with the nasal cavity between and the mouth cavity underneath in the center. When the eye cavity has a fracture on the bottom, orbital fat tissue can herniate into the sinus cavity underneath. This is called a “blowout fracture” of the eye cavity and would be typical for a fist fight or when a shrapnel from a gunshot wound had entered the eye cavity. Both CT and MRI scans will depict this reliably.
Treatment
The first seconds and minutes count most after an eye injury. If there was an eye injury from eye contact with a lie (=alkaline chemical compound) the eye needs to be washed for at least 5 minutes (better up to 15 or 20 minutes) with tap water. One way to do this is to simply fill a sink with water and open and close the eyes many times to dilute the chemical and flush it out at the same time. Have the patient assessed by an ophthalmologist on an emergency basis.
Treatment for various eye injuries
Eye lid lacerations: If there is a laceration of the margin of an eyelid, an eye surgeon has to do an exact repair with the help of an operating microscope.
Metal foreign body in the cornea: The eye specialist removes the foreign body under an anesthetic. Subsequently the specialist also removes any rust spot carefully (from an iron or steel piece).
Corneal ulcer: If the person wears a contact lens, the eye specialist has to remove this and treat the eye with Polytrim or erythromycin ointment. The eye specialist follows the injured person every day until the injury healed. There is a great danger that the cornea perforates, if there is no close follow up.
Penetrating Wounds of the Eye
Some of these injuries can be very ugly. Here is a text that deals with this topic in more detail.
Burns of the eye: The eye specialist must identify what burn injury did occur. If there was exposure to extreme heat, the eye lids will have suffered burns. But the cornea can also suffer some degree of burning. There is a complexity to these injuries. They need close supervision by an eye specialist, often with hospitalization for several days.
Various sports injuries: In this link to common sports injuries it is described what tests and procedures need to be done to remedy the situation as much as it can be remedied.
References
1. The Merck Manual: Blunt injuries to the eye.
2. Ferri: Ferri’s Clinical Advisor: Instant Diagnosis and Treatment, 2004 ed., Copyright © 2004 Mosby, Inc.
3. Rakel: Conn’s Current Therapy 2004, 56th ed., Copyright © 2004 Elsevier