To clarify, in the following there is a list of the more common brain cancer tumor types. In fact, this list includes both the central nervous system as well as the spinal cord. In particular, it shows that the more common brain tumors are glioblastoma and astrocytoma, all of which are indeed based on histology investigation of biopsy samples.
To explain, the following tables of frequency of occurrence are based on data from Ref.1 and 2. Notably, neurosurgeons operated on patients with various brain tumors and to be sure sent the surgical samples for histological analysis to the pathologist. Specifically, the percentages relate to how often a particular brain or spinal cord tumor cancer type was found among all of the brain or spinal cord cancers.
Brain tumors
Glioblastoma multiforme : 30%
Astrocytoma : 20%
Other gliomas
Oligodendroma, ependymoma : 5%
Meningioma : 20%
Schwannoma (acoustic neuromas) : 10%
Pituitary : 5%
Other tumors : 10%
______________________________________________________
Spinal cord tumors
Schwannoma : 25%
Meningioma : 35%
Ependymoma : 15%
Astrocytoma : 10%
Other Tumors : 15%
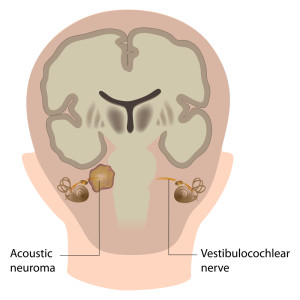
For one thing, some of these are benign tumors such as acoustic neuroma (image shown above), which is a schwannoma and is a benign tumor (not cancerous). That is to say, however, that there is only so much space within the human skull. For instance, the increased intracranial pressure within the brain with these tumors becomes a danger to the person who has it. To repeat, for this reason even a benign brain tumor can become an emergency that requires surgery.
References
1. Cancer: Principles &Practice of Oncology. 4th edition. Edited by Vincent T. DeVita, Jr. et al. Lippincott, Philadelphia,PA, 1993. Chapter on brain cancer.
2. Cancer: Principles&Practice of Oncology. 5th edition, volume 2. Edited by Vincent T. DeVita, Jr. et al. Lippincott-Raven Publ., Philadelphia,PA, 1997. Chapter on brain cancer.
3. Conn’s Current Therapy 2004, 56th ed., Copyright © 2004 Elsevier
4. Ferri: Ferri’s Clinical Advisor: Instant Diagnosis and Treatment, 2004 ed., Copyright © 2004 Mosby, Inc