Introduction
Papilledema is an acute swelling of the optic nerve head in the back of the eye.
It is almost always on both eyes at the same time. It is an acute emergency that should be treated right away by an eye specialist. Here are some common causes of papilledema.
Signs and symptoms
There are no symptoms initially. There may be associated other symptoms from the underlying diseases such as headaches with many brain tumors or other space occupying brain lesions.
Diagnostic test
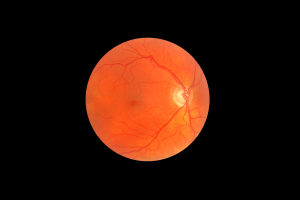
When careful visual testing is done, an increased blindspot would be noticed (visual field testing). Fundoscopic examination (examination with an ophthalmoscope or a slit lamp) shows this image (thanks to www.kellogg.umich.edu for this image).
Causes of papilledema
| brain tumor or abscess |
| meningitis |
| head trauma (concussion or bleeding) |
| encephalitis |
| severe high blood pressure |
| other diseases, which cause elevated intracranial pressure |
Treatment
Blood pressure needs to be taken and treated aggressively, if this is the cause for the papilledema.
With head trauma or other causes of increased intracranial pressure this needs to be reversed by removal of a brain tumor, by a shunt procedure, by diuretic therapy or other measures.
The treatment is directed at the identified causal condition. If high blood pressure is the cause, this is aggressively treated, possibly in an Intensive Care Unit setting for a few days until the danger of loss of eyesight is over. If meningitis is the cause, this needs to be treated aggressively.
References:
1. The Merck Manual: Papilledema (thanks to www.merckmanuals.com for this link).
2. Ferri: Ferri’s Clinical Advisor: Instant Diagnosis and Treatment, 2004 ed., Copyright © 2004 Mosby, Inc.
3. Rakel: Conn’s Current Therapy 2004, 56th ed., Copyright © 2004 Elsevier