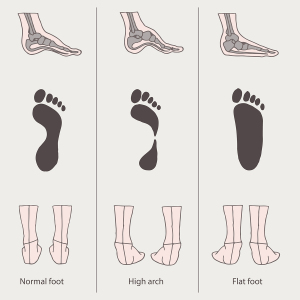
Flat foot is a structural variation of the foot where the foot arch at the inner aspect of the foot is flattened. This leads to foot arch and foot pain. Sometimes a physician may falsely diagnose a flat foot in infants as they have a prominent fat pad in the medial longitudinal arch.
However, with tiptoeing the arch is normalizing showing that it was a false diagnosis of a “flat foot” and the infant really has a normal infant foot. This peculiarity and the associated wide-based gait and “foot pronation” normalizes itself at the age of 2.5 years (Ref.2).
Normal foot development in a child
The child’s foot changes its morphology and becomes more like the adult foot by the age of 8 years. A good pair of children’s shoes will is all that the child needs. Diagnostic tests usually are not needed as the diagnosis is based on the clinical examination. If beyond the age of 8 years there is a foot arch, which is fallen at the inside of the longitudinal arch, then this needs to be treated with appropriate insoles and this will usually take care of the foot pain (Ref. 1).
References
1. ABC of rheumatology, second edition, edited by Michael L. Snaith , M.D., BMJ Books, 1999. Chapter 5.
2. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 270.
3. Wheeless’ Textbook of Orthopaedics: http://www.wheelessonline.com/
4. The Merck Manual, 7th edition, by M. H. Beers et al., Whitehouse Station, N.J., 1999. Chapter 60, p.487.
5. Goldman: Cecil Textbook of Medicine, 21st ed.(©2000)W.B.Saunders
6. Ferri: Ferri’s Clinical Advisor: Instant Diagnosis and Treatment, 2004 ed., Copyright © 2004 Mosby, Inc.
7. Rakel: Conn’s Current Therapy 2004, 56th ed., Copyright © 2004 Elsevier