A group of German researchers reported that they found a cure for lupus with CAR T-cell therapy. CAR T-cell therapy has made a big difference for patients with B cell lymphomas. Survival rates are much better with this type of therapy.
Brief review of the use of CAR T-cell therapy for lymphoma patients
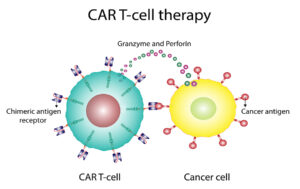
CAR T-cell therapy is the abbreviation for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell therapy. Briefly, with lymphomas the body’s immune system has become ineffective in eliminating lymphoma cells. But with the CAR T-cell therapy one treatment can cure a lymphoma patient. The reason is that researchers used a specific virus to insert genetic material into the patient’s own T cells. This produces transmembrane proteins on the surface of the T cells. The transformed T cells can now recognize specific tumor proteins, which kill the tumor cells.
CAR T-cell therapy for autoimmune diseases like lupus
A group of researchers from Germany had the idea to use the CAR T-cell therapy with autoimmune diseases such as lupus. This is the topic of this discussion. 15 patients with severe autoimmune diseases (lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis and idiopathic inflammatory myositis) had an impressive response to the CAR T-cell therapy. It lasted at least 15 months and seems to be ongoing.
Side effects
Patients tolerated the CAR T-cell therapy fairly well with only minor side effects due to lower circulating B lymphocytes. Infections occurred in 14 patients. They consisted of urinary tract infections, respiratory infections and pneumonia, which the doctors treated with antibiotica. Two patients experienced herpes reactivation at 6 months and 12 months following treatment. The FDA is currently investigating whether chimeric antigen receptor CAR T-cell immunotherapy could cause secondary cancers. However, this complication only occurred so far in patients with cancer, not in patients with autoimmune diseases.
How the CAR T-cell treatment works
The researchers noted that the CAR T-cell treatment worked by providing an “entire reset of B cells,” which possibly was even a cure for these 15 patients. Previously these patients ran out of treatment options as they got worse despite treatments. The following publications described these patients in more detail: Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases earlier this year, Nature Medicine in 2022, and the New England Journal of Medicine in 2021.
Course after CAR T-cell treatment
All of the 15 patients with autoimmune diseases were heavily treated in the past with various treatment modalities, but none succeeded. Only the use of CAR T-cell therapy was successful in treating their multi organ autoimmune disease. The average age of the clinical subjects was 36 years, which is fairly young compared to lymphoma patients. Only one treatment was necessary for a cure of their previously intractable autoimmune disease.
Conclusion
CAR T-cell therapy, an immunotherapy for lymphoma patients, was applied for difficult to treat autoimmune patient with lupus. Their standard treatments failed and researchers used one CAR T-cell therapy to treat their autoimmune disease. All 15 patients responded successfully with minimal side effects. CAR T-cell therapy is the abbreviation for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell therapy. Researchers used a specific virus to insert genetic material into T cells. This produces transmembrane proteins on the surface of the T cells. These altered T cells can kill lymphoma cells, but they can also rid the body of B cells that produce autoantibodies. This is how the 15 patients with autoimmune conditions were cured.